Navigating Success: The Triple Diamond Framework in Tech Design
The Triple Diamond Framework provides a structured yet flexible approach to design, aligning seamlessly with the dynamic landscape of technology. Its emphasis on user-centricity, risk mitigation, and innovation makes it an invaluable tool for tech companies striving for excellence in their design processes. By adopting this framework, companies not only enhance the quality of their products but also establish a robust foundation for sustained success in the competitive tech industry.
Understanding the Triple Diamond Framework:
In the fast-paced world of technology, where innovation is paramount, a robust design framework is critical for achieving success. The Triple Diamond Framework, a design thinking approach developed by the Design Council, UK, has emerged as a guiding beacon for tech companies aiming to create user-centric, impactful solutions. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the Triple Diamond Framework, its concrete applications, implementation strategies, research questions, and the compelling benefits it offers compared to alternative design processes.
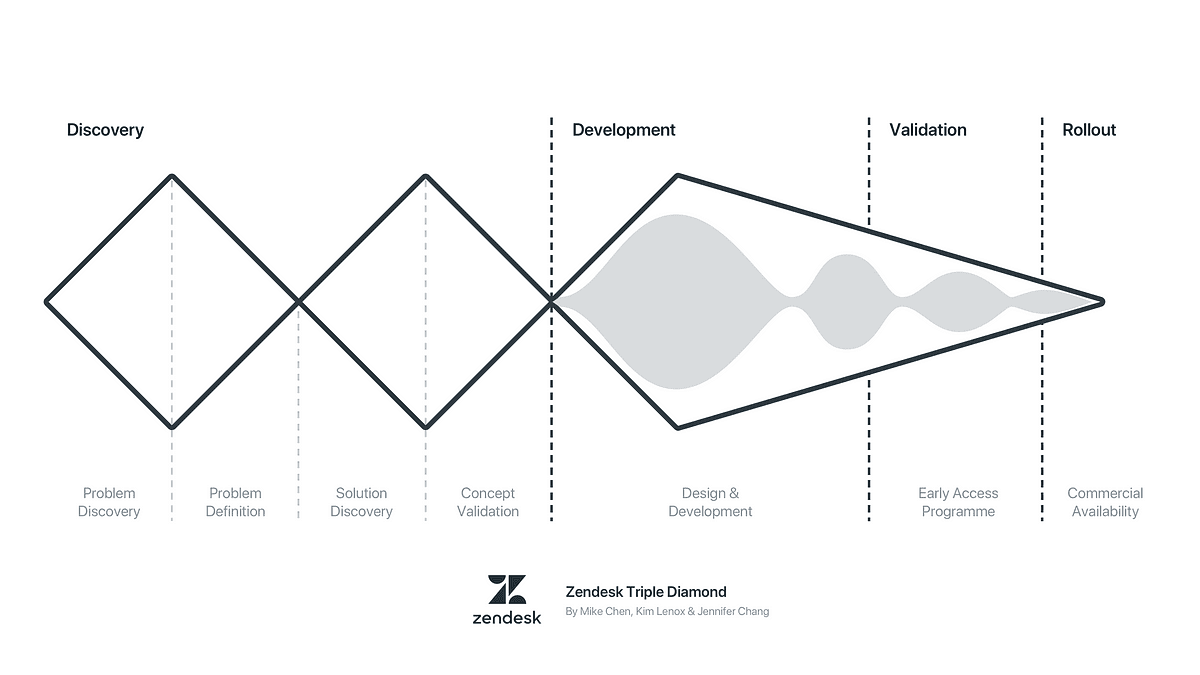
The Triple Diamond Framework is structured into three key stages: Discover, Define, and Develop. Each stage represents a phase in the design process, focusing on a specific aspect of product or service development.
Discover:
Objective: Uncover insights and define the problem space.
Implementation: Conduct extensive user research, surveys, and interviews. Utilize empathy mapping and journey mapping to understand user experiences.
Example: In developing a new health app, the Discover stage might involve researching user habits, health concerns, and preferences. User interviews and surveys can reveal insights into existing pain points in managing health data.
Research Questions:
- What are the current challenges users face in managing their health data?
- How do users interact with existing health apps, and what frustrations do they encounter?
Define:
Objective: Synthesize gathered information to define the core problem.
Implementation: Create user personas, ideate potential solutions, and narrow down to a specific problem statement.
Example: For the health app, the Define stage could involve identifying that users struggle with tracking multiple health metrics in a cohesive manner.
Research Questions:
- What are the commonalities among user challenges identified in the Discover stage?
- What aspects of health tracking are most crucial for users?
Develop:
Objective: Generate, prototype, and test potential solutions.
Implementation: Develop prototypes, conduct user testing, and iterate based on feedback.
Example: Building on the health app, the Develop stage would include creating a prototype that integrates various health metrics seamlessly.
Research Questions:
- How do users respond to the prototype’s interface and features?
- What additional features or adjustments would enhance user experience?
Benefits of the Triple Diamond Framework:
User-Centricity:
- Benefit: Prioritizes user needs, leading to products that resonate with the target audience.
- Example: Apple’s iterative design process for the iPhone, focuses on user feedback and preferences.
Risk Mitigation:
- Benefit: Identifies and addresses potential challenges early in the design process.
- Example: Tesla’s approach to prototyping and testing autonomous driving features to ensure safety and functionality.
Innovation and Agility:
- Benefit: Encourages creativity and flexibility, fostering innovation.
- Example: Google’s continuous refinement of search algorithms based on user behavior and evolving needs.
Service Design in Action: Resolving Tech Challenges
Digital Banking Transformation:
- Challenge: An established bank faced the challenge of transitioning to a digital-first model.
- Service Design Solution: Service designers mapped the entire customer journey, identifying opportunities for digital integration and creating an omnichannel experience. The result was a seamless transition that retained existing customers and attracted new ones.
Healthcare Appointment Scheduling:
- Challenge: A healthcare provider struggled with a disjointed appointment scheduling system.
- Service Design Solution: Service designers collaborated with IT teams to revamp the scheduling system. By integrating user-friendly interfaces and automation, they significantly reduced appointment errors and improved patient satisfaction.
E-learning Platform Enhancement:
- Challenge: An e-learning platform faced issues with user engagement and technology adoption.
- Service Design Solution: Through service design workshops, the team identified pain points in the user journey. They implemented personalized learning paths, interactive features, and real-time feedback mechanisms. The result was increased user engagement and improved learning outcomes.
